
Understand some of the potential opportunities offered by the emerging Hydrogen economy for your polymer-related business activities
Polymers and polymer composites have been essential materials for the energy industry for many years fulfilling functions where it is either impossible or very difficult for metals to be effective. Non-metallic materials now form an essential building block of all energy projects, used for weight reduction, corrosion resistance, sealing functionality and a host of other reasons.
Noting that the emergence of the ‘hydrogen economy’ presents further opportunities for the use of polymers and their unique properties, these new applications will inevitably present challenges which must be considered in design.
The report focuses on the use of polymers in the storage, transportation and distribution of hydrogen. This sector represents an area where there are a range of significant hurdles to overcome for hydrogen to become mainstream as a source of power, the potential for the use of ammonia is considered.
The report provides a review of this industry application from a polymer materials perspective. Whether a polymer supplier, processor, or end user, it examines the main materials challenges for greater use of polymers and composites. It explores areas where polymers are currently used, and why, as well as potential future applications and what is required to bring these to fruition. Covered in more detail will be the more critical polymer properties for applications in this industry including, diffusion and permeation, cryogenic and low temperature performance, tribological performance and erosion.
As the industry increases pace in putting appropriate standards and test methods in place, the report considers those which are relevant to the evaluation and approval of polymers.
Get a head-start in understanding the opportunities and challenges with how your products may interact with hydrogen – its storage, transportation, and distribution.
Elsewhere in the Energy Sector much has been achieved in particular for the use of polymers to seal and contain liquids and gases. Examples include polymeric pipes for gas transportation, elastomeric seals for ensuring leak-free joints and polymeric bearings to ensure smooth operation of valves.
Significant experience has been gained with natural gas and gases associated with the production of oil and natural gas such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide.

However, Hydrogen presents some new challenges: this well-known gas does not exist naturally on earth but due to its physical characteristics makes an ideal energy carrier and storage media.
In spite of being highly flammable in air, hydrogen is rather unreactive when in contact with polymers and elastomers and unlike other gases, its interaction with polymeric materials is centred less upon chemical degradation and more upon effective and safe containment.
Since produced hydrogen is an energy source, losses of the gas due to permeation or gross leakage, represent additional costs and loss of efficiency.
The principal use of hydrogen for energy is in a hydrogen fuel cell, although it is also feasible to burn directly as a replacement for methane. Fuel cells use hydrogen, reacted with oxygen across a thin membrane to generate electricity. Such systems can be built in a range of sizes to provide power for domestic heating, vehicular transportation, and even small domestic appliances.
Hydrogen may also be used for direct combustion to generate heat as a replacement for natural gas (methane). In the UK, 100% hydrogen domestic heating trials are already being conducted nationwide.
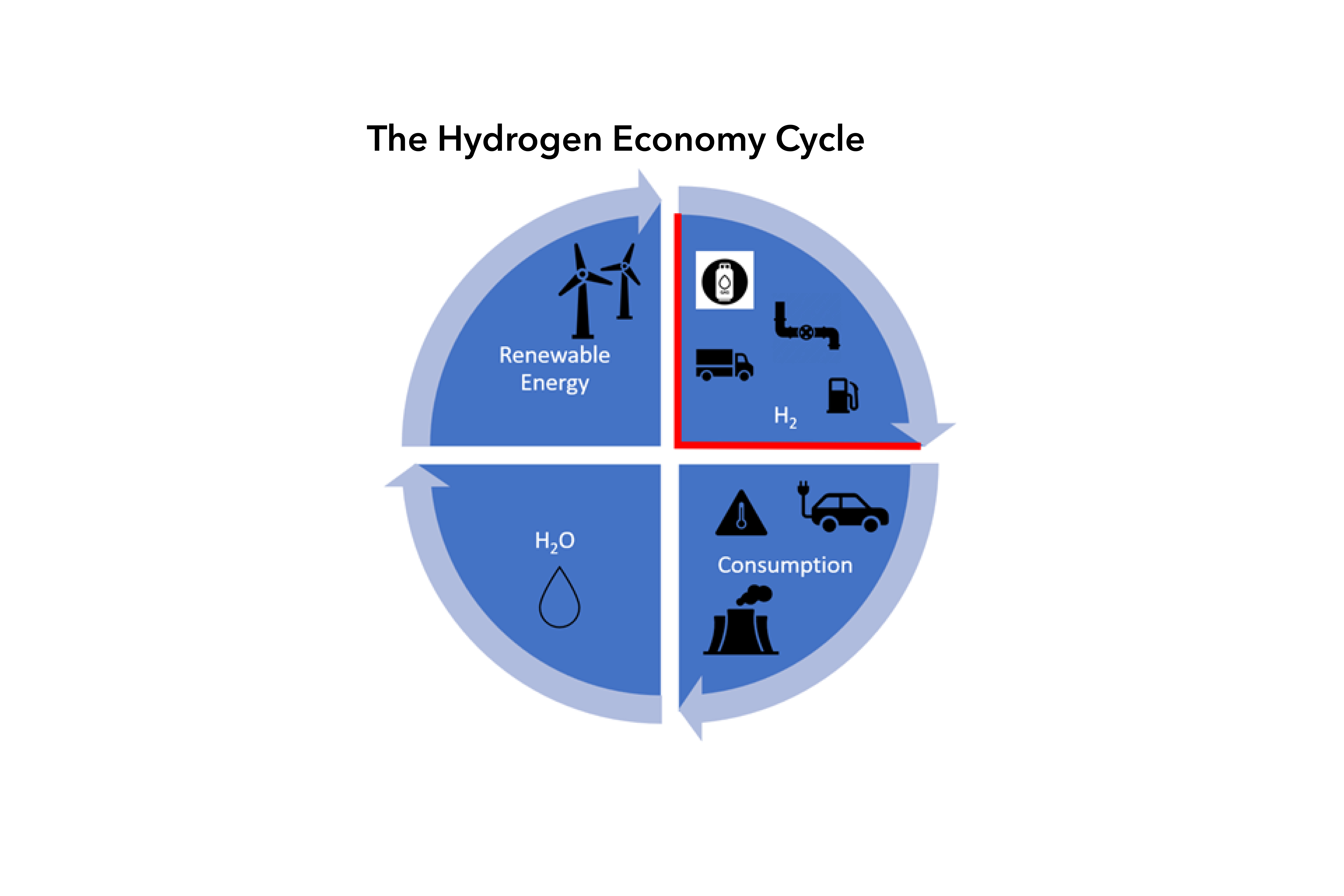
Each part of this industry increasingly has a need for polymeric materials for a wide range of application.
The AMI research into the topic of hydrogen has focussed upon the use of polymers in the second quadrant of the cycle and highlighted with a red outline: this covers the storage, transportation and distribution of hydrogen. This sector represents an area where there are a range of significant hurdles to overcome for hydrogen to become mainstream as a source of power, including the use of ammonia.
Get in touch
Need support? We’re ready to help you:
- Identify new marketing opportunities
- Tap into emerging technologies
- Improve your strategic decision making
It all starts with a conversation.
